Conditions d’achèvement
Molecules that share the same crude formula are isomeric molecules. They differ from each other by their developed formulas.
There are three main types of isomerisms:
• structural isomers
• geometric plane isomerisms
• steric isomers (stereoisomers)
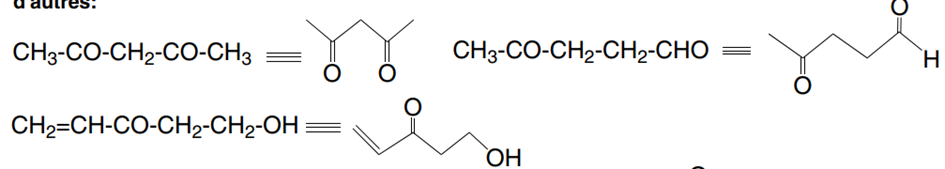
As an example, for the crude formula C5 H8O2we can find the following isomers, among
others:
II-1-Structural isomerisms
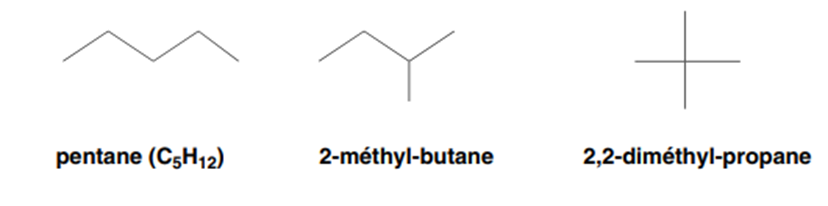
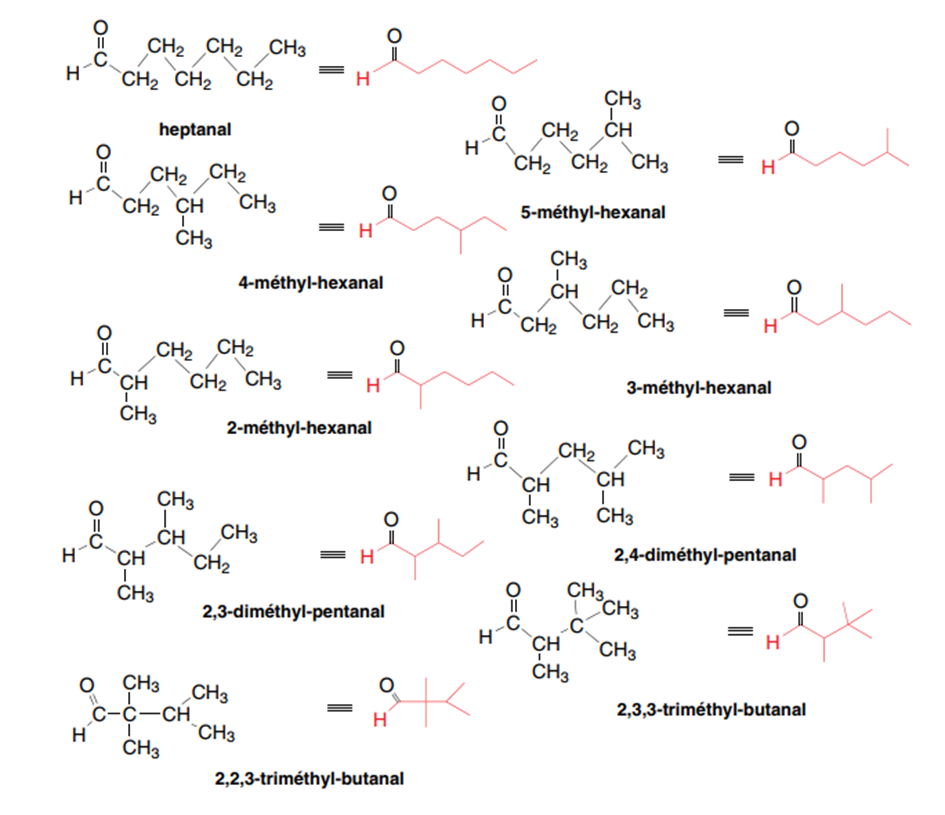
II-1-1-Chain isomerism
The chain isomers differ from each other by the assembly of carbon atoms which form what we call the carbon chain or the carbon skeleton of the molecule.
Example
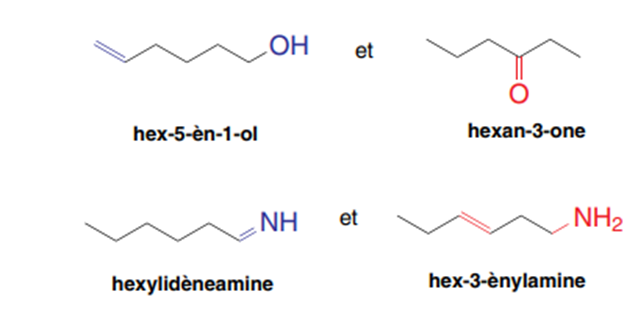
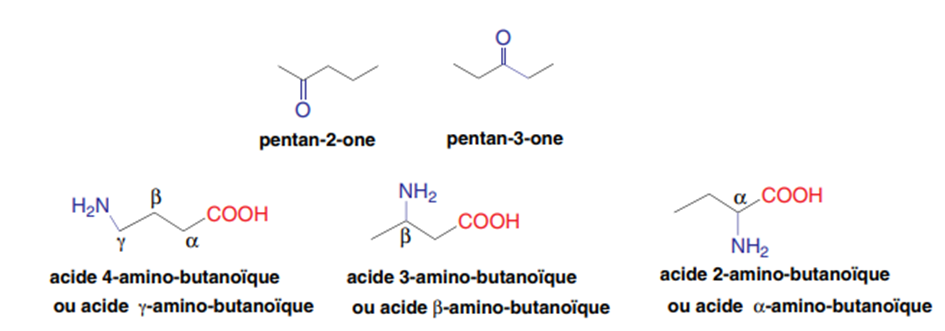
II-1-2-Positional isomerism
The movement of one or more functions on the same carbon chain leads to positional isomers.
Exp:
II-1-3-Functional isomerism
The corresponding isomers have the same carbon chain, but differ between them by the nature of their function(s).